Data and Computer Communications (Chapter 1)
اسلاید 1: William Stallings Data and Computer CommunicationsChapter 1Introduction
اسلاید 2: A Communications ModelSourcegenerates data to be transmittedTransmitterConverts data into transmittable signalsTransmission SystemCarries dataReceiverConverts received signal into dataDestinationTakes incoming data
اسلاید 3: Simplified Communications Model - Diagram
اسلاید 4: Key Communications TasksTransmission System UtilizationInterfacingSignal GenerationSynchronizationExchange ManagementError detection and correctionAddressing and routingRecoveryMessage formattingSecurityNetwork Management
اسلاید 5: Simplified Data Communications Model
اسلاید 6: NetworkingPoint to point communication not usually practicalDevices are too far apartLarge set of devices would need impractical number of connectionsSolution is a communications network
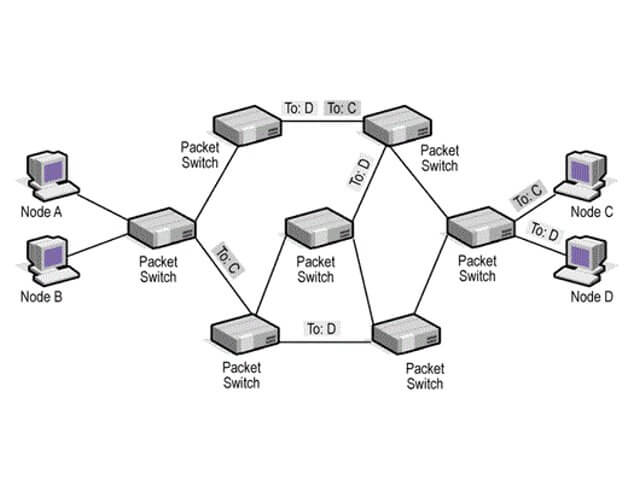
اسلاید 7: Simplified Network Model
اسلاید 8: Wide Area NetworksLarge geographical areaCrossing public rights of wayRely in part on common carrier circuitsAlternative technologiesCircuit switchingPacket switchingFrame relayAsynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
اسلاید 9: Circuit SwitchingDedicated communications path established for the duration of the conversatione.g. telephone network
اسلاید 10: Packet SwitchingData sent out of sequenceSmall chunks (packets) of data at a timePackets passed from node to node between source and destinationUsed for terminal to computer and computer to computer communications
اسلاید 11: Frame RelayPacket switching systems have large overheads to compensate for errorsModern systems are more reliableErrors can be caught in end systemMost overhead for error control is stripped out
اسلاید 12: Asynchronous Transfer ModeATMEvolution of frame relayLittle overhead for error controlFixed packet (called cell) lengthAnything from 10Mbps to GbpsConstant data rate using packet switching technique
اسلاید 13: Integrated Services Digital NetworkISDNDesigned to replace public telecom systemWide variety of servicesEntirely digital domain
اسلاید 14: Local Area NetworksSmaller scopeBuilding or small campusUsually owned by same organization as attached devicesData rates much higherUsually broadcast systemsNow some switched systems and ATM are being introduced
اسلاید 15: ProtocolsUsed for communications between entities in a systemMust speak the same languageEntitiesUser applicationse-mail facilitiesterminalsSystemsComputerTerminalRemote sensor
اسلاید 16: Key Elements of a ProtocolSyntaxData formatsSignal levelsSemanticsControl informationError handlingTimingSpeed matchingSequencing
اسلاید 17: Protocol ArchitectureTask of communication broken up into modulesFor example file transfer could use three modulesFile transfer applicationCommunication service moduleNetwork access module
اسلاید 18: Simplified File Transfer Architecture
اسلاید 19: A Three Layer ModelNetwork Access LayerTransport LayerApplication Layer
اسلاید 20: Network Access LayerExchange of data between the computer and the networkSending computer provides address of destinationMay invoke levels of serviceDependent on type of network used (LAN, packet switched etc.)
اسلاید 21: Transport LayerReliable data exchangeIndependent of network being usedIndependent of application
اسلاید 22: Application LayerSupport for different user applicationse.g. e-mail, file transfer
اسلاید 23: Addressing RequirementsTwo levels of addressing requiredEach computer needs unique network addressEach application on a (multi-tasking) computer needs a unique address within the computerThe service access point or SAP
اسلاید 24: Protocol Architectures and Networks
اسلاید 25: Protocols in Simplified Architecture
اسلاید 26: Protocol Data Units (PDU)At each layer, protocols are used to communicateControl information is added to user data at each layerTransport layer may fragment user dataEach fragment has a transport header addedDestination SAPSequence numberError detection codeThis gives a transport protocol data unit
اسلاید 27: Network PDUAdds network headernetwork address for destination computerFacilities requests
اسلاید 28: Operation of a Protocol Architecture
اسلاید 29: TCP/IP Protocol ArchitectureDeveloped by the US Defense Advanced Research Project Agency (DARPA) for its packet switched network (ARPANET)Used by the global InternetNo official model but a working one.Application layerHost to host or transport layerInternet layerNetwork access layerPhysical layer
اسلاید 30: Physical LayerPhysical interface between data transmission device (e.g. computer) and transmission medium or networkCharacteristics of transmission mediumSignal levelsData ratesetc.
اسلاید 31: Network Access LayerExchange of data between end system and networkDestination address provisionInvoking services like priority
اسلاید 32: Internet Layer (IP)Systems may be attached to different networksRouting functions across multiple networksImplemented in end systems and routers
اسلاید 33: Transport Layer (TCP)Reliable delivery of dataOrdering of delivery
اسلاید 34: Application LayerSupport for user applicationse.g. http, SMPT
اسلاید 35: TCP/IP Protocol Architecture Model
اسلاید 36: OSI ModelOpen Systems InterconnectionDeveloped by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO)Seven layersA theoretical system delivered too late!TCP/IP is the de facto standard
اسلاید 37: OSI LayersApplicationPresentationSessionTransportNetworkData LinkPhysical
اسلاید 38: OSI v TCP/IP
اسلاید 39: StandardsRequired to allow for interoperability between equipmentAdvantagesEnsures a large market for equipment and softwareAllows products from different vendors to communicateDisadvantagesFreeze technologyMay be multiple standards for the same thing
اسلاید 40: Standards OrganizationsInternet SocietyISOITU-T (formally CCITT)ATM forum
اسلاید 41: Further ReadingStallings, W. Data and Computer Communications (6th edition), Prentice Hall 1999 chapter 1Web site for Stallings bookwww.shore.net/~ws/DCC6e.htmlWeb sites for IETF, IEEE, ITU-T, ISOInternet Requests for Comment (RFCs)Usenet News groupscomp.dcom.*comp.protocols.tcp-ip















نقد و بررسی ها
هیچ نظری برای این پاورپوینت نوشته نشده است.